Khám phá các bộ truyền động dẫn đầu: Acme, ốc vít bóng, và hơn thế nữa

Các nhà lãnh đạo là một phần không thể thiếu của vô số hệ thống truyền động trong các ngành công nghiệp như sản xuất, robot, hàng không vũ trụ, và hơn thế nữa. Là một thành phần tích hợp trong bộ truyền động tuyến tính, loại khách hàng tiềm năng bạn sử dụng có thể ảnh hưởng đáng kể đến hiệu suất tổng thể của bộ truyền động của bạn. Từ độ chính xác đến độ tin cậy, các thuộc tính của các loại chì khác nhau có thể đóng vai trò là người thay đổi trò chơi trong lĩnh vực kỹ thuật. Hiểu các tính năng và ứng dụng riêng biệt của từng loại là rất quan trọng để lựa chọn trình độ dẫn thích hợp nhất cho thiết kế bộ truyền động của bạn.
Trong cuộc thám hiểm toàn diện này, chúng tôi sẽ đi sâu vào ba loại chì nổi bật - ACME, ốc vít bóng và ốc vít lăn hành tinh - và làm sáng tỏ những khác biệt chính, các tính năng độc đáo và các ứng dụng mẫu mực trong bối cảnh bộ truyền động. Cuối cùng, bạn sẽ không chỉ thành thạo ngôn ngữ của các nhà lãnh đạo mà còn được trang bị kiến thức để tối ưu hóa hiệu suất của bộ truyền động trong các dự án của bạn.
Acme Leadscrews
Những người tiên phong của chuyển động tuyến tính
Acme Leadscrews đã ra lệnh cho chuyển động tuyến tính trong nhiều thế kỷ, nhờ sự đơn giản và mạnh mẽ của họ. Được sử dụng trong một loạt các hệ thống truyền động, thiết kế của ACME Leadscrew có cấu hình ren hình thang, cung cấp hiệu quả trong việc chuyển chuyển động quay sang chuyển động tuyến tính. Các luồng thường rộng hơn với các dây dẫn lớn hơn, cho phép áp dụng mô -men xoắn cao hơn mà không cần liên kết trục.
Các ứng dụng trong hệ thống truyền động
Thiết kế đơn giản và khả năng mô-men xoắn của ACME Leadscrews làm cho chúng rất phù hợp cho các ứng dụng yêu cầu chuyển động tuyến tính theo cách được kiểm soát nhưng có thể chịu đựng được mức độ ma sát đáng kể hơn. Điều này làm cho chúng trở thành một lựa chọn phổ biến trong các ứng dụng như hệ thống nâng, người định vị và máy ép, trong đó tốc độ ít quan trọng hơn so với việc duy trì vị trí chính xác đang được tải.
Ưu điểm và nhược điểm
Acme Leadscrews cung cấp các lợi ích như hiệu quả chi phí, đơn giản và mức độ tùy chỉnh cao. Với ít thành phần hơn, chúng cũng dễ bảo trì hơn. Tuy nhiên, hiệu quả tương đối thấp hơn của chúng do ma sát tăng lên và sự không phù hợp của chúng đối với các ứng dụng tốc độ cao có thể được coi là nhược điểm.
Nghiên cứu trường hợp của bộ truyền động: FIRGELLI Bộ truyền động tuyến tính điện
Một bộ truyền động mẫu mực khai thác sức mạnh của Acme Leadscrews là FIRGELLI Bộ truyền động tuyến tính điện. Bằng cách kết hợp những người dẫn đầu này, FIRGELLI Các bộ truyền động duy trì sự cân bằng tinh tế giữa sức mạnh và độ chính xác, làm cho chúng hoàn hảo cho các ứng dụng từ tự động hóa gia đình đến các cơ sở công nghiệp.
Vít bóng
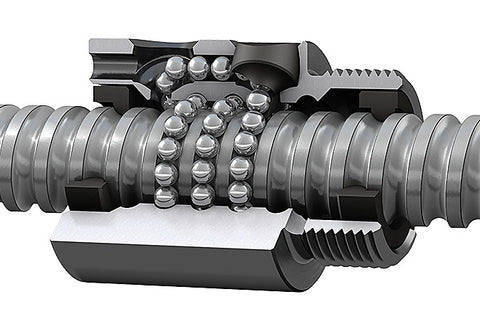
Chính xác được nhân cách hóa
Các ốc vít bóng đã cách mạng hóa khái niệm công nghệ chì bằng cách giới thiệu các yếu tố lăn, điển hình là những quả bóng thép, giữa ốc vít và đai ốc. Sự thay đổi khéo léo này làm giảm đáng kể ma sát, cho phép chuyển động mượt mà hơn, độ chính xác cao hơn và hiệu quả cơ học cao hơn so với các chì ACME.
Các ứng dụng trong hệ thống truyền động
Các hệ thống truyền động đòi hỏi độ chính xác và hiệu quả cao, chẳng hạn như các hệ thống được tìm thấy trong máy CNC, máy bay và thiết bị sản xuất chất bán dẫn, được hưởng lợi rất nhiều từ công nghệ tiên tiến của vít bóng. Khả năng xử lý tải trọng cao, truyền chuyển động với ma sát bên trong rất thấp và hoạt động ở tốc độ cao khiến chúng trở thành một lựa chọn cho nhiều ngành công nghiệp chính xác cao.
Ưu điểm và nhược điểm
Việc sử dụng vòng bi bóng dẫn đến giảm mạnh ma sát trượt, tạo điều kiện cho một hoạt động gần như bảo trì. Vít bóng cũng cung cấp truyền tải năng lượng hiệu quả cao, làm cho chúng phù hợp cho các ứng dụng nhạy cảm với năng lượng. Tuy nhiên, chi phí trả trước của họ và độ nhạy cảm với cả bụi bẩn hoặc ô nhiễm nhỏ có thể đặt ra những thách thức.
Nghiên cứu trường hợp của bộ truyền động: Giường máy CNC
Trong bối cảnh của Gia công CNC, tầm quan trọng của độ chính xác và độ lặp lại cao không thể được cường điệu hóa. Hệ thống vít bóng trong giường máy CNC đáp ứng các tiêu chí này bằng cách cung cấp chuyển động tuyến tính phù hợp, chính xác cao, rất quan trọng đối với công việc phức tạp thường được thực hiện trong chế tạo kim loại và các hoạt động gia công chính xác khác.
Vít con lăn hành tinh
Chinh phục cực đoan
Các ốc vít lăn hành tinh là lớp công nghệ chì ưu tú, được thiết kế cho các điều kiện khắc nghiệt trong đó tải nặng nhất, tốc độ cao nhất và độ chính xác đòi hỏi khắt khe nhất là điều kiện tiên quyết. Trục vít và đai ốc kết hợp nhiều con lăn có ren, dẫn đến một lợi thế cơ học vượt qua cả ốc vít ACME và bóng.
Các ứng dụng trong hệ thống truyền động
Với khả năng phát triển mạnh dưới lực đẩy cao và tải trọng sốc, các ốc vít lăn hành tinh tìm thấy môi trường sống tự nhiên của chúng trong các hệ thống truyền động của máy móc hạng nặng, như tua -bin thủy điện, thang máy trong các nhà máy điện hạt nhân và hệ thống phóng không gian. Hiệu quả đặc biệt và tuổi thọ đặc biệt của họ khi tăng cường làm cho chúng lý tưởng để định vị các bề mặt điều khiển trong máy bay, đặc biệt là máy bay chiến đấu và máy bay thương mại.
Ưu điểm và nhược điểm
Thiết kế mạnh mẽ của các ốc vít con lăn hành tinh cho phép chúng xử lý các tải trọng cực cao với độ chính xác và hiệu quả. Khả năng của họ để hoạt động dưới tốc độ cao và với các yêu cầu bảo trì thấp củng cố vị trí của họ như là một lựa chọn cho các ứng dụng hiệu suất cao. Tuy nhiên, sự phức tạp của chúng và nhu cầu dung sai sản xuất nghiêm ngặt có thể chuyển thành chi phí cao hơn.
Nghiên cứu trường hợp của bộ truyền động: Hệ thống điều khiển máy bay
Các hệ thống truyền động bề mặt điều khiển trong máy bay hiện đại dựa vào hiệu suất của các ốc vít lăn hành tinh. Các ốc vít này là không thể thiếu trong các bề mặt điều khiển di chuyển, chẳng hạn như máy bay và thang máy, với tốc độ, lực và phản ứng tối thiểu cần thiết, do đó đảm bảo tính toàn vẹn an toàn và hoạt động của máy bay.
Phần kết luận
Chủ đề tục ngữ của thành công
Chọn đúng hướng dẫn cho hệ thống truyền động của bạn là một quyết định quan trọng với ý nghĩa sâu rộng đối với hiệu suất, độ tin cậy và hiệu quả. Mặc dù mỗi loại lãnh đạo có những lợi thế và ứng dụng lý tưởng độc đáo, tất cả chúng đều đóng một vai trò quan trọng trong việc cho phép chuyển động tuyến tính trong thế giới hiện đại.
Bằng cách hiểu sự phức tạp của thiết kế và ứng dụng chì, bạn có thể điều chỉnh các hệ thống truyền động của mình để đáp ứng các yêu cầu cụ thể của bạn, cho dù đó là độ chính xác trong nhà máy chế tạo chất bán dẫn hoặc cung cấp năng lượng cho thủy lực trong một báo chí công nghiệp nặng. Tham gia với các nhà sản xuất hàng đầu và cập nhật về những tiến bộ mới nhất trong công nghệ LeadScrew sẽ đảm bảo rằng các hệ thống truyền động của bạn vẫn luôn đi đầu trong ngành của bạn.
Trong lĩnh vực năng động của kỹ thuật và tự động hóa, một hằng số giữ đúng: chìScrew có thể chỉ là một thành phần nhỏ, nhưng nó quay các bánh xe lớn của sự đổi mới và tiến bộ. Cho dù đó là ACME cho độ tin cậy của nó, các ốc vít bóng cho độ chính xác hoặc vít con lăn hành tinh cho hiệu suất mạnh mẽ, chủ đề bạn chọn để ràng buộc vận mệnh của bộ truyền động của bạn sẽ dệt nên câu chuyện về thành công của bạn. Khi bạn bắt tay vào dự án truyền động tiếp theo của mình, hãy chắc chắn xem xét đúng với người dẫn đầu khiêm tốn, vì đó là người anh hùng im lặng trong các câu chuyện chuyển động tuyến tính được viết bởi các kỹ sư trên toàn cầu.